研究業績
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 73, 12877-12886 (2025)
Insights into the imidaclothiz biodegradation by the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete sordida YK-624 under ligninolytic conditions
著者
R. Yin, M. Chang, R. Ma, J. Wang, N. Wang, T. Xiao, H. Hirai
カテゴリ
学術論文
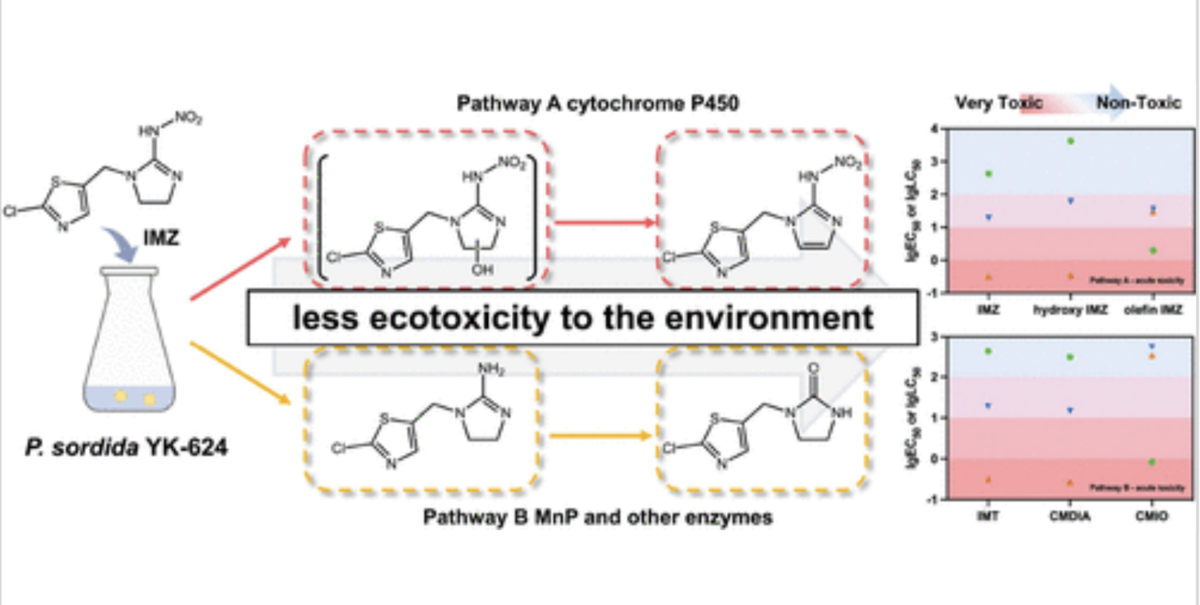
Abstract
Imidaclothiz (IMZ), an innovative neonicotinoid insecticide, has attracted significant interest due to its environmental persistence and consequent ecological implications. In this research, the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete sordida YK-624 was used to degrade IMZ, unveiling a novel fungal degradation mechanism. The results demonstrated that IMZ was efficiently degraded by P. sordida YK-624. Transcriptomic analysis revealed that IMZ-induced stress triggered a cascade of enzymatic and cellular defense responses that are instrumental in facilitating its biodegradation. Through inhibitor experiments and enzyme activity profiling, cytochrome P450 and manganese peroxidase (MnP) were identified to play crucial roles in IMZ biodegradation. Additionally, three metabolites were isolated and identified by NMR, and two innovative degradation pathways involving hydroxylation and nitro reduction were proposed. Toxicity assessment suggested the reduced environmental risk of IMZ after its degradation by P. sordida YK-624. These findings provided insights into the IMZ degradation mechanism and highlighted the potential of white-rot fungi in neonicotinoid bioremediation.